A Comparative Analysis of 5 Engineering Disciplines: Electronics, Electrical, Mechanical, Civil, and Chemical

Introduction:
Choosing the right engineering discipline can be a daunting task for aspiring engineers. With numerous options available, each with its unique characteristics and career prospects, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the differences between them. In this blog, we’ll delve into a comparative analysis of five prominent engineering disciplines: Electronics, Electrical, Mechanical, Civil, and Chemical. By examining various aspects such as curriculum, job opportunities, and industry trends, we aim to provide valuable insights to help individuals make informed decisions about their career paths.
Electronics Engineering:
Electronics engineering focuses on the design and development of electronic devices, circuits, and systems. Students in this discipline learn about semiconductor theory, digital and analog electronics, and signal processing. Careers in electronics eng’g often involve working in industries such as telecommunications, consumer electronics, and semiconductor manufacturing. Professionals in this field may design and test electronic components, develop embedded systems, or work on advanced technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI).
Electrical Engineering:
Electrical engineering deals with the study and application of electricity, electromagnetism, and electronics. It encompasses a broad range of topics, including power systems, control systems, and renewable energy. Graduates in electrical eng’g. can pursue careers in diverse sectors such as power generation, telecommunications, and automation. They may work on projects involving the design of electrical networks, the development of renewable energy technologies, or the implementation of smart grid systems.
While both electronics and electrical eng’g. deal with the study and application of electricity and electromagnetism, they have distinct focuses and areas of expertise. Let’s delve deeper into the differences between these two eng’g. disciplines:
Electronics Engineering:
Focus on Small-Scale Devices: Electronics engineering primarily focuses on the design, development, and application of small-scale electronic components, circuits, and systems. This includes devices such as transistors, diodes, integrated circuits (ICs), and microcontrollers.
Signal Processing and Control Systems: Electronics engineers often work with signals, both analog and digital, and specialize in signal processing techniques such as filtering, modulation, and amplification. They also design control systems for various applications, including robotics, automation, and consumer electronics.
Digital and Analog Electronics: Electronics engineering covers both digital and analog electronics. Digital electronics deals with discrete signals represented by binary digits (bits), whereas analog electronics focuses on continuous signals. Electronics engineers are proficient in designing circuits for both digital and analog applications.
Applications in Consumer Electronics and Embedded Systems: Electronics engineering plays a crucial role in the development of consumer electronics products such as smartphones, tablets, computers, and home appliances. Additionally, electronics engineers work extensively on embedded systems, which are specialized computing devices embedded within larger systems or products.
Electrical Engineering:
Focus on Large-Scale Power Systems: Electrical engineering primarily deals with the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electrical power on a large scale. This includes power generation plants, electrical grids, and distribution networks.
Power Systems and Control: Electrical engineers specialize in power systems eng’g, which involves designing and maintaining electrical infrastructure to ensure reliable and efficient power supply. They also work on control systems for power generation and distribution, optimizing performance and maintaining stability.
Renewable Energy and Sustainable Technologies: With the growing emphasis on sustainability, electrical engineers are increasingly involved in renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power generation. They play a critical role in developing and implementing sustainable energy solutions to address environmental challenges.
High Voltage and High Power Applications: Electrical engineering encompasses high voltage and high power applications, including electrical machines, transformers, and power electronics. Electrical engineers design and analyze systems capable of handling high voltages and currents safely and efficiently.
Key Differences:
Scale and Application: Electronics engineering focuses on small-scale electronic devices and systems, while electrical engineering deals with large-scale power systems and infrastructure.
Signal Processing vs. Power Systems: Electronics engineering emphasizes signal processing and control systems, whereas electrical engineering focuses on power generation, transmission, and distribution.
Consumer Electronics vs. Power Generation: Electronics engineers often work in industries such as consumer electronics, telecommunications, and embedded systems, while electrical engineers are involved in power generation, utilities, and renewable energy sectors.
Digital and Analog vs. Power Systems: Electronics engineering covers both digital and analog electronics, while electrical eng’g specializes in power systems and high voltage applications.
In summary, while electronics and electrical eng’g share common foundations in electricity and electromagnetism, they diverge in their applications, scales of operation, and areas of expertise. Electronics eng’g deals with small-scale electronic devices and signal processing, while electrical eng’g focuses on large-scale power systems and infrastructure. Both disciplines offer unique opportunities for specialization and career development within the broader field of eng’g.
Mechanical Engineering:
Mechanical engineering is one of the oldest and broadest eng’g disciplines, focusing on the design, analysis, and manufacturing of mechanical systems. Students in this field learn about thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and materials science. Mechanical engineers work in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where they design and optimize machinery, engines, and mechanical components. They may be involved in product development, testing, or research and development (R&D) activities.
Civil Engineering:
Civil engineering revolves around the planning, design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure projects such as buildings, bridges, roads, and water systems. Students in this discipline study structural eng’g, geotechnical eng’g, and transportation eng’g. Civil engineers play a crucial role in shaping the built environment, addressing societal needs, and ensuring public safety. They work in various sectors, including construction, transportation, and environmental eng’g, where they oversee projects from conception to completion.
Chemical Engineering:
Chemical engineering combines principles of chemistry, physics, and mathematics to design and optimize processes for the production, transformation, and utilization of chemicals and materials. Students in this field learn about reactor design, mass transfer, and process control. Chemical engineers work in industries such as pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and environmental eng’g, where they develop sustainable processes, improve efficiency, and ensure product quality. They may be involved in research, process design, or plant operations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, each engineering discipline offers unique opportunities and challenges, catering to different interests and skill sets. Whether you’re passionate about electronics, fascinated by machines, or interested in building infrastructure, there’s an eng’g field that aligns with your aspirations. By understanding the distinctions between disciplines like electronics, electrical, mechanical, civil, and chemical eng’, individuals can make informed decisions about their educational and career paths. Ultimately, the choice of eng’g discipline should be based on personal interests, career goals, and societal impact, paving the way for a fulfilling and rewarding profession in the ever-evolving field of engineering.
We also include some review materials for students. Please check this link.
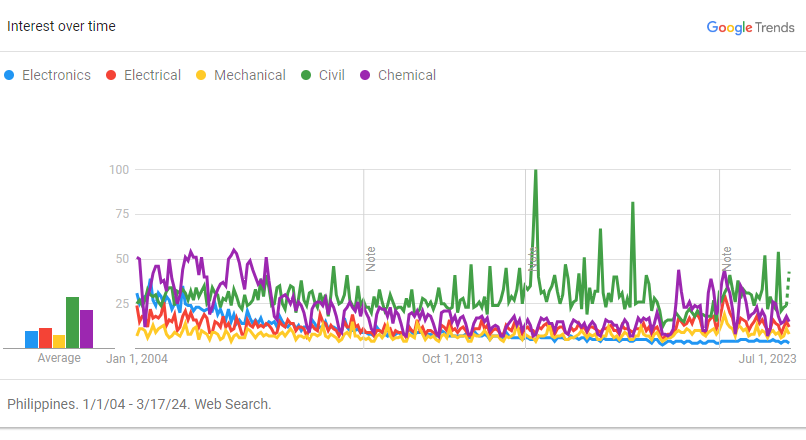
Below is the graph of interest for different engineering fields. Please visit this link, for further details.







Add Comment